01.2023 Life Guide
2023 Global Financial Market Outlook
Far Eastern International Bank / Gao Yixun

.jpg) In 2022, the inflation pressure will continue to test the fiscal policies of various countries. According to Bloomberg and international indicators, the trend of global economic slowdown has not changed. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) predicted that 1/3 of the economies will face recession. When can inflation cool down? Will interest rates continue to rise this year? This issue of "Finance Column" analyzes the development situation of the financial market for you.
In 2022, the inflation pressure will continue to test the fiscal policies of various countries. According to Bloomberg and international indicators, the trend of global economic slowdown has not changed. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) predicted that 1/3 of the economies will face recession. When can inflation cool down? Will interest rates continue to rise this year? This issue of "Finance Column" analyzes the development situation of the financial market for you.After two years of good prospects, 2022 will be a tough year for personal investment and business operation. Although the central banks' interest rate hikes had been expected, their plans could not keep up with the changes. Russia invaded Ukraine, pushing up the prices of raw materials; China, the manufacturing place of major components and products in the world, has taken strict epidemic control measures, resulting in supply chain disruption; In 2022, the annual growth of the consumer price index of the United States will hit a new 40 year high. Faced with heavy inflationary pressure, the Federal Reserve System can only accelerate the pace of interest rate increase to curb inflation.
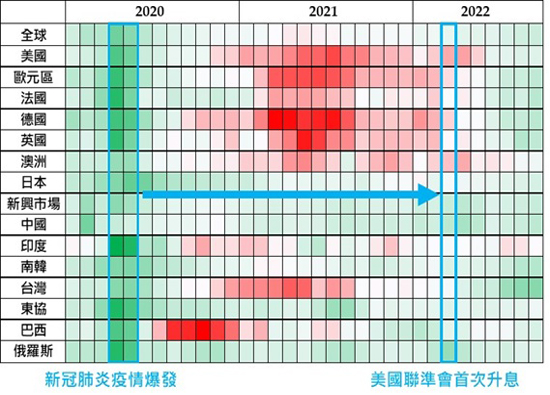
Figure 1 Manufacturing procurement manager index of major global economic systems (2020/1~2022/9, source: Bloomberg, 2022/10)
The manufacturing purchasing manager index (PMI) of major global economic systems can reflect the prosperity and decline of the manufacturing industry, which can be used to judge the strength of national economic activities. The weaker the economic activities, the more dark green they are, and vice versa. When the COVID-19 broke out, the prosperity declined rapidly due to the strict closure policy adopted by various countries. However, the Federal Reserve System quickly cut interest rates and introduced unrestricted quantitative easing measures. In addition, governments of all countries offered positive fiscal policies. The boom quickly rebounded (especially in mature countries, because of the abundance of epidemic prevention materials and economic resources). PMI in manufacturing industry soon changed from dark green to light green, or even red.
However, any policy has its side effects. After the large-scale rescue of the market, the rapid recovery of the economy has led to demand exceeding supply, and the inflation risk is slowly rising. In March 2022, the Federal Reserve System began to raise interest rates, but the pace was slow because of fear that the fragile economy would decline again. Nevertheless, the inflationary pressure still rose rapidly after various "accidents". The Federal Reserve System was forced to raise interest rates rapidly to respond, so the economy began to decline again. Take Taiwan as an example. In the third quarter of 2022, export orders declined by 1.1% compared with the same period last year, and are growing for nine consecutive quarters.
In 2023, the global economy will continue to slow down and the risk of recession will remain high
In the new year, we all hope that the global economy and financial markets can get rid of the downturn. However, as long as the government's policies are inclined to tighten, the momentum of economic growth will be affected.
1. Inflation will cool down, but it is difficult to relax the tight monetary policy
In 2023, the financial market is most concerned about whether inflation can cool down, which affects whether the pace of the central bank's sharp interest rate increase will slow down. According to the estimate of Bloomberg on consumer price index (hereinafter referred to as CPI), the annual growth rate of global CPI in 2022 will be 7.40%, significantly higher than 4.7% in 2021, and it will decline in 2023, reaching 4.8%. The CPI of European and American countries will also be at a very high level in 2022, which will also cool down in 2023. It is worth noting that China's CPI will rise significantly in 2022, but it will be at a relatively low level compared with that of European and American countries, indicating that the inflationary pressure is relatively light. Therefore, the People's Bank of China will adopt a relatively loose monetary policy.
Most people may think that after the inflation pressure cools down, the pace of the central bank's interest rate increase can be slowed down. However, it may cause inflation to get out of control and repeat the stagnating inflation of the 1970s. At that time, more intense monetary policy must be adopted, instead increasing the pressure of economic recession. Therefore, even if the interest rate increase in 2023 decreases, it will not end immediately. Even if it ends, the central bank will maintain the interest rate at a relatively high level for a period of time, and simultaneously carry out quantitative monetary policy tightening until it is determined that inflation can fall back to the central bank's target area (taking the United States as an example, the inflation target of the Federal Reserve System is 2%, while according to Bloomberg, the annual growth rate of the U.S. CPI in 2023 is 4%).
2. The global political situation has changed, and the policy is inadequate
Since the central bank is fighting against inflation and the government is facing a downturn, if it wants to use fiscal policy to stimulate the economy, the financial market will certainly vote against it. When the former British Prime Minister Liz Truss took office in 2022, he announced a large-scale tax reduction plan, which caused the soaring interest rate of British government bonds, the devaluation of the pound against the dollar, almost triggered a financial crisis, and made Truss the shortest serving British Prime Minister. Therefore, in the face of the economic environment of high inflation and low growth, governments can only reduce the inflationary pressure as much as possible.
In addition, geopolitical instability will continue to affect the global economy. In particular, the sanctions imposed by European and American countries on Russia and the restrictions imposed by the United States on the development of China's science and technology industry will lead to a different pattern of global politics from that in the past 10 years. In addition, the rise of protectionism and the decline of globalization will add more uncertainty to the economy in 2023.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) mentioned in the World Economic Outlook Report in October 2022 that more than 1/3 of the global economies will decline in 2022 or 2023, while the three largest economies, the United States, the European Union and China, will continue to be at a standstill. The IMF's chief economist added: The worst is yet to come. The economic forecast model released by Bloomberg in October 2022 also shows that the US economy will almost certainly fall into recession in the next 12 months.
3. The global economy is expected to move towards a U-shaped recovery rather than a V-shaped recovery
If the global economy really falls into recession in 2023, the chances of repeating the V-shaped reverse recovery in 2008 and 2020 are quite low. First, the measures taken by the Federal Reserve System are different. Second, China's economy may experience low growth. Third, the Ukrainian Russian war may continue.
In September 2008, Lehman Brothers announced bankruptcy. In addition to rapid interest rate reduction, Federal Reserve System announced quantitative easing (QE) to stabilize the financial market. In the follow-up, not only did the interest rate remain low, but also QE was implemented twice to slowly repair the global economy. In March 2020, the COVID-19 broke out, and liquidity risks appeared again in the financial market. The Federal Reserve System not only cut interest rates, but also directly announced unlimited QE. QE since 2008 has led to a capital explosion in the global financial market. If the money is not collected, inflation cannot be curbed at all. Therefore, Powell, Chairman of Federal Reserve System, and his officials said that it is unlikely to cut interest rates in 2023. In other words, the possibility of relying on the central bank to rescue the market and economy is quite low.
On the other hand, the Uzbek Russian war affected the supply of global energy and food. Russia took various measures to reduce the supply of natural gas to European countries, resulting in soaring prices and rapid economic decline in Europe. Even if the war stops, the economic sanctions imposed by both sides will not be lifted in a short time. China, the world's second largest economy, will adopt policies to stimulate the economy in 2022, but the real estate market will be sluggish. With the rising cost of manufacturing and domestic and foreign political factors, international enterprises will gradually move their production bases to Southeast Asian countries such as Vietnam. It is unlikely that they will return to the economic glory of the past by relying on exports and domestic consumption.
In 2022, all industries will face the pressure of high inventory, especially the science and technology industry. However, most companies say that this is not a change in the industrial structure, but a normal business cycle. In the second quarter of 2022, TSMC said that the semiconductor industry does face the problem of high inventory, and it will not have the opportunity to digest to a reasonable level until the second quarter of 2023. Obviously, we are in a period of declining prosperity. We must wait for demand to cool down, supply to return to normal level, and inflation to gradually decline, so that the prosperity will have the opportunity to bottom out.
#