07.2021 Life Guide
Economic outlook for the second half of 2021
Far Eastern International Bank / Huang Baiwei

Look back to the first half of 2021, although Taiwan stock market marked the breakthrough, the novel coronavirus pneumonia has been more serious, and many investors' confidence has been put out. In the second half of 2021, what important trends should we pay attention to in order to save ourselves from danger and accumulate wealth for ourselves?
The novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreak is still uncertain after more than a year’s effort of epidemic prevention. In Europe and the United States, the progress of vaccination is encouraging. Many state governments in the United States even said that tourism related activities will be expected to restart in the summer. However, in terms of Asia and emerging markets, many countries are still fighting hard. The differentiation of the epidemic trend may affect the performance of financial markets in the future. On the whole, most of the economy of various countries are on the track of recovery, and the progress is faster and faster. In addition, the loose policies of the central banks of the major countries remain unchanged, and the huge capital market is still fermenting, supporting the world to move towards the post epidemic era.
Review of the first half of 2021: the trend of global epidemic differentiation, vaccination rate of emerging countries is seriously backward
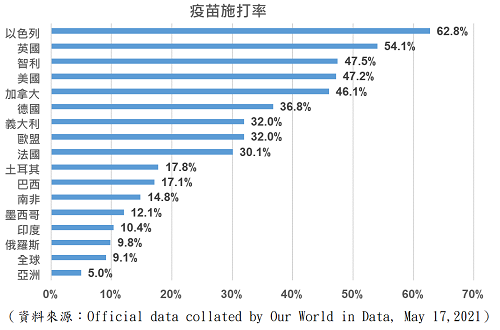
Vaccination in some countries (such as the United States, the United Kingdom and Israel) has made rapid progress, not only effectively reducing the domestic infection rate, but also controlling the mortality at a low level. However, in addition to the above-mentioned countries, the number of people who have got at least one dose of vaccine in most emerging market countries is still less than 20% of the country's total population. Vaccine supply and logistics transportation have become the main problems of these countries.
Under the condition of insufficient vaccination, the epidemic broke out again in Latin America (such as Argentina, Brazil and Colombia), emerging Europe (such as Turkey) and Asia (such as India, Philippines and Taiwan). In particular in India, which is seriously short of medical equipment and materials, there is not only a large number of infected people, the epidemic even has spread to the surrounding South and Southeast Asian countries, New pressure on the local economy. Before the epidemic was brought under control and vaccination rates rose, the overall economic recovery in emerging markets was uneven and the progress of recovery was delayed.
Focus of market concern in the second half of 2021: epidemic, inflation and monetary tightening
1. Mature countries take the lead in reaching the standard, and vaccines are expected to be released to emerging countries.
With the coverage of Pfizer, Modena and AZ vaccines, the fight against the epidemic in the United States, which was the most serious part in the past, has reached a critical turning point. According to the latest guidelines of the Centers for Disease Control and prevention of the United States, people who have received two doses of the vaccine don’t need to wear masks or maintain social distancing, which means that as long as they have received two doses of the vaccine and have no abnormalities in observation after two weeks, they can resume their life style before the epidemic; US President Biden also recently said that in addition to 60 million doses of AZ vaccine, at least 20 million doses of other vaccines will be sent by the end of June to assist in global epidemic prevention. That is to say, as the vaccination in mature countries gradually reaches the standard, the surplus vaccines are expected to be released to other emerging countries to help them control the epidemic situation. It is estimated that the emerging countries will also achieve mass immunization in 2022. After all, as President Biden said, "we know that the United States is not really safe until the global epidemic is really under control."
2. Inflation interferes as expected, stock market volatility become serious
In addition to the epidemic, the most concern of the market is inflation. Last year, economic activity was halted due to the impact of the epidemic, and the global price level declined significantly. This year, with the gradual reduction of the impact of the epidemic and the recovery of the global economy and demand. However, the supply chain has been faced with different degrees of impact. The news of lack of work, lack of materials has been heard frequently. In addition, from blizzards and hurricanes in Texas, to the fire in Japan's automotive chip factory, to the crisis in Japan Incidents such as the stranding of EVA freighter on the Suez Canal and the infection of Indian crew have all impacted the tight supply chain step by step, forcing the recent rise of international crude oil and raw material prices.
The longer delivery time of suppliers and the higher prices of raw materials also increase the production costs of factories, which in turn increase the product prices. If enterprises pass on the rising cost to consumers, it will cause inflation doubts. Not only that, the rising inflation expectation has made the bond yields of major economies rise at the same time. The market is worried that the increase of financing cost of enterprises will affect the revenue and profit, which leads to the increase of global stock market volatility since the second quarter.
Officials from the Federal Reserve System and other central banks said that the current rise in yields is a normal phenomenon triggered by economic recovery, and they will continue to pay attention to the trend of yields in the future. The Federal Reserve System does not want to intervene in the market because of the fluctuation of the single market, but will observe the overall financial environment, so it will not change the loose monetary policy until the economy fully recovers.
3. The market is worried about the tightening of monetary policy. Is it far from us to raise interest rates?
With the advent of the vaccine and the gradual recovery of economic activity, the yield of 10-year U.S. government bonds has soared from 0.91% at the beginning of this year to 1.78%. The market is worried that this will lead to an increase in corporate borrowing costs, and the stock markets of various countries have reversed. The soaring prices of energy and raw materials have also raised inflation expectations. Some emerging countries (such as Turkey, Brazil, Russia, etc.) have chosen to raise interest rates in response to the soaring inflation and high US bond yields, but Asian countries are an exception. This is mainly because over the past few decades, the economic constitution of Asian countries has been in a leading position in developing countries, and inflation is relatively low. The Asian financial crisis in 1997 and the financial tsunami in 2008 both made Asian countries learn from the past and actively adjust their national economic constitution. Therefore, although all countries are facing the pressure of rising inflation, so far no country in emerging Asia has chosen to raise interest rates.
In terms of mature countries, the inflation index - PCE referenced by the Federal Reserve System of the United States increased at an annual rate of 1.8% in March, which is close to the original target of 2% of the Federal Reserve System. However, the Federal Reserve System proposed a new inflation policy in August last year, allowing the inflation rate to moderately exceed 2% and the inflation target of 2% on average "over a period of time" before the interest rate will be raised. Although the Federal Reserve System didn’t indicate the time limit, there is still a long way to go before the goal of the Federal Reserve System, whether it is an average of 1.5% in three months, 1.4% in six months or 1.3% in one year. Therefore, the chairman of the Federal Reserve System has repeatedly stressed that the current economic recovery in the United States is uneven, the unemployment rate is still at a high point, and there is still "a long way to go" to achieve the goals of employment and inflation. Moreover, inflation only reflects temporary factors, and it is not time to discuss reducing the scale of debt purchase or raising interest rates.
There were so many ways for things to get better.
On the whole, economic recovery will contribute to the performance of risk assets. Although the market is worried about epidemic control, rising inflation and monetary tightening, the central banks of mature countries such as Europe and the United States continue to maintain loose policies, which should help to support their market performance. Therefore, in asset allocation, it is suggested to focus on the "multi asset" with both income and anti volatility.
In terms of vaccination, mature countries have faster vaccination speed and are expected to complete mass immunization in the second half of the year. At that time, economic activities will gradually return to the normal level before the epidemic. Therefore, investment can give priority to mature countries and be allocated to stocks such as raw materials stocks related to the recovery of manufacturing industry or consumer stocks benefiting from the stabilization of consumer confidence. As for emerging markets, the difference between countries is still the key. The current epidemic may lead to slow recovery in some markets (Latin America and India). However, exports from other regions (especially northeast Asia) will continue to be strong, and it is expected that they will still have a good performance. Therefore, in terms of investment proposals, we can take regional assets as the direction and avoid single country. In addition, in the bond market, with the overall economic recovery, the yield is expected to rise in a stepwise upward trend. Coupled with the continuous improvement of the credit quality of corporate bonds, high-yield bonds with short duration are expected to become the focus of investment.