03.2024 Life Guide
Low dose chest computed tomography for early detection of lung cancer
Dr. Zheng Shilong, Department of Thoracic Medicine at Far Eastern Memorial Hospital /

 In recent years, lung cancer has consistently ranked first in cancer mortality in Taiwan, mainly divided into two categories: small cell and non-small cell, with the latter being the most common (about 90%). Lung adenocarcinoma is also the most common, accounting for 58.17% and 87.3% of male and female cases, respectively. It is worth noting that over 50% of these lung cancer patients do not smoke, and over 90% of female patients have never smoked. In the past decade, there has been a trend towards younger cancer patients.
In recent years, lung cancer has consistently ranked first in cancer mortality in Taiwan, mainly divided into two categories: small cell and non-small cell, with the latter being the most common (about 90%). Lung adenocarcinoma is also the most common, accounting for 58.17% and 87.3% of male and female cases, respectively. It is worth noting that over 50% of these lung cancer patients do not smoke, and over 90% of female patients have never smoked. In the past decade, there has been a trend towards younger cancer patients.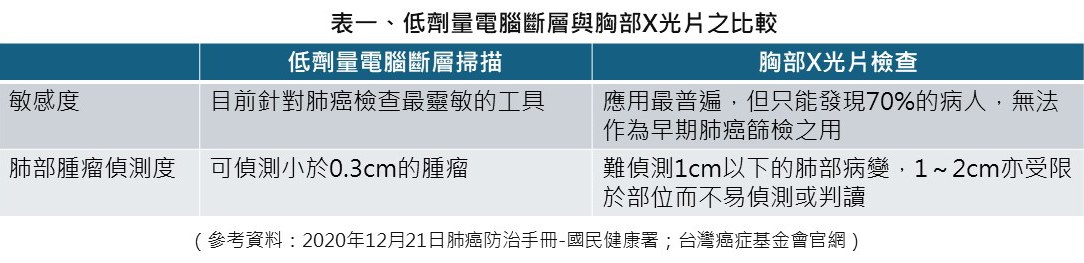 According to research, if lung cancer screening services can be provided in a timely manner, and lesions can be detected early and surgically removed, the cure rate of tumors with a diameter of about 1 cm is 85-90% (no recurrence for 5 years). However, in the early stages of lung cancer, there are no symptoms. Traditional lung X-ray examinations, which are most commonly used in clinical practice, have low sensitivity and are not easy to detect tumors smaller than 1 cm. When the disease is detected, it is usually in the late stage, leading to poor patient survival rates.
According to research, if lung cancer screening services can be provided in a timely manner, and lesions can be detected early and surgically removed, the cure rate of tumors with a diameter of about 1 cm is 85-90% (no recurrence for 5 years). However, in the early stages of lung cancer, there are no symptoms. Traditional lung X-ray examinations, which are most commonly used in clinical practice, have low sensitivity and are not easy to detect tumors smaller than 1 cm. When the disease is detected, it is usually in the late stage, leading to poor patient survival rates.With the advancement of medical diagnostic technology, there are more and more methods for screening lung cancer, including sputum cytology, chest X-ray examination, low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT), magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography, bronchoscopy, and biomarker detection through blood or exhaled gases. Among them, low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) has international evidence, and a large research project in the United States has also confirmed that only it has extremely high sensitivity, can detect lung lesions as small as 0.3 cm, and can screen early lung cancer patients among severe smokers, making it the best tool for early detection of lung cancer.
 The benefits of low-dose computed tomography screening for lung cancer
The benefits of low-dose computed tomography screening for lung cancerReducing the mortality rate of lung cancer: The results of the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial in the United States showed that low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) lung cancer screening can help reduce lung cancer mortality by up to 20%; The results of the European lung cancer screening test also reflect that the mortality rate of male lung cancer has decreased by 24%, and the mortality rate of female lung cancer has decreased even more.
Discovering early lung cancer and improving quality of life: Late stage lung cancer can easily lead to related symptoms and reduce quality of life, whether it is the disease itself or the treatment method. Low dose computed tomography (LDCT) lung cancer screening can detect lesions early, reduce the proportion of disease progression to advanced stages, and thereby improve the quality of life of patients.
Diagnosis of other early diseases: In addition to lung cancer, low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) can also screen for other early diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and coronary artery calcification.
Radiation exposure is lower than conventional: the radiation exposure of a conventional CT scan is about 100 times that of X-rays, while the radiation exposure of a low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) scan is only 1/5 of that of a conventional CT scan.
Screening reminder
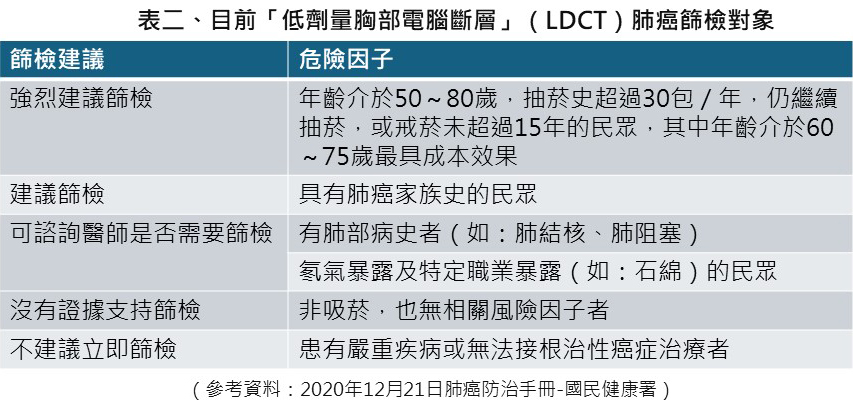
The purpose of screening for lung cancer is to detect the cancer before the patient presents symptoms, as the earlier the diagnosis of lung cancer is made, the more effective the treatment can be, thereby reducing the mortality rate of cancer. Therefore, it is recommended to use low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) as the primary screening tool, and even if there are no symptoms, regular screening should be conducted, especially for high-risk populations who should consider developing screening plans early.
In order to enable early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of high-risk populations, the Ministry of Health and Welfare Bureau of Health Promotion has launched lung cancer screening services since July 2022, with low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) as the fifth cancer screening project. Far Eastern Memorial Hospital is also involved, providing severe smokers aged 50-74, males aged 50-74, and females aged 45-74, High risk individuals with a family history of lung cancer undergo low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) every 2 years. Those who meet the eligibility criteria for subsidies can inquire about thoracic and surgical outpatient services.
epilogue
The annual death toll from lung cancer has exceeded 10000 people, and the standard incidence rate of lung cancer in women has been increasing year by year, which is more significant than in men. We urge everyone to dispel the misconception that "without smoking or a family history, one will not develop lung cancer", develop healthy lifestyle habits, stay away from risk factors, and undergo non-invasive low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) screening, early detection, diagnosis, and treatment to maintain health.
#